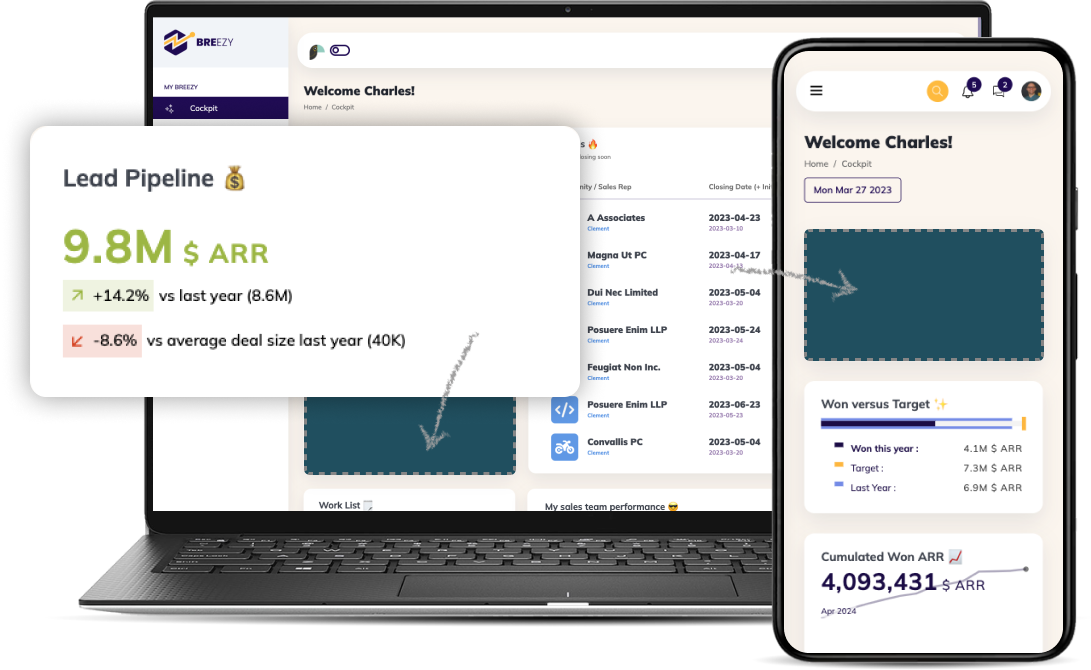
The business landscape of today is driven by data. Whatever your business or industry, data empowers strategic decision-making, uncovers new revenue streams, and uncovers hidden waste generators that are eating into your bottom line.
However, data alone is not sufficient to achieve any of these objectives. To accomplish this, you will need to establish a tech stack that connects all relevant data sources. Unfortunately, choosing data analytics tools and platforms that enable your business to move forward is not an easy task.
For selecting platforms and tools that are appropriate for your business objectives, we discuss evaluation criteria, key features, and other considerations in this article.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Data
Due to the wide range of use cases, applications, and industries covered, it is difficult to come up with an exhaustive list of selection criteria. The following suggestions may assist in narrowing the search:
- Decide what your goals are. Although it is easy to get caught up in the possibilities of analytic tools, defining your program's primary goals and developing a strategy that is well thought out is much more crucial than the tools themselves. Why is data strategy important to you? What do you hope to achieve with it? Build your toolkit around the core goals of your business, be it real-time asset monitoring or a deeper understanding of what your customers need.
- Consider the use cases specific to your industry. Become familiar with the analytic platforms, tools, and capabilities others in your industry are using to solve problems and create opportunities.
- Put yourself in the shoes of the end user. Investing in analytics tools requires a comprehensive strategy that involves everyone within the organization, from the C-suite to your customer service representatives. Analyze the impact of analytics on different roles within your organization. What users require simplified solutions to assist them in making decisions? Are you in need of marketing or sales-specific tools? Are you proficient in data science?
Types of Data Analytic Tools and Key Features
Despite their broad scope, the tools tend to fall into a few key categories:
Customer-Facing Analytics
Customer-facing analytics are becoming increasingly popular, both for products that embed them and as a feature requested by consumers. A traditional business intelligence (BI) system allows for ad hoc analysis and self-service, while a customer-facing analytics system provides end users with a packaged experience. As part of customer-facing analytics, data producers (enterprises that own the data) and data consumers (end users or customers) can interact with one another.
In customer-facing analytics, data and visualizations enable interactive analysis within the bounds of a packaged experience by defining and delivering visualizations to the end user. It is possible to deliver customer-facing analytics in a variety of ways, such as interactive dashboards, web applications, or mobile applications. The shift in analytics workloads toward customer-facing analytics provides various actionable insights and methods of generating revenue. A variety of data types are handled by them from a variety of data sources.
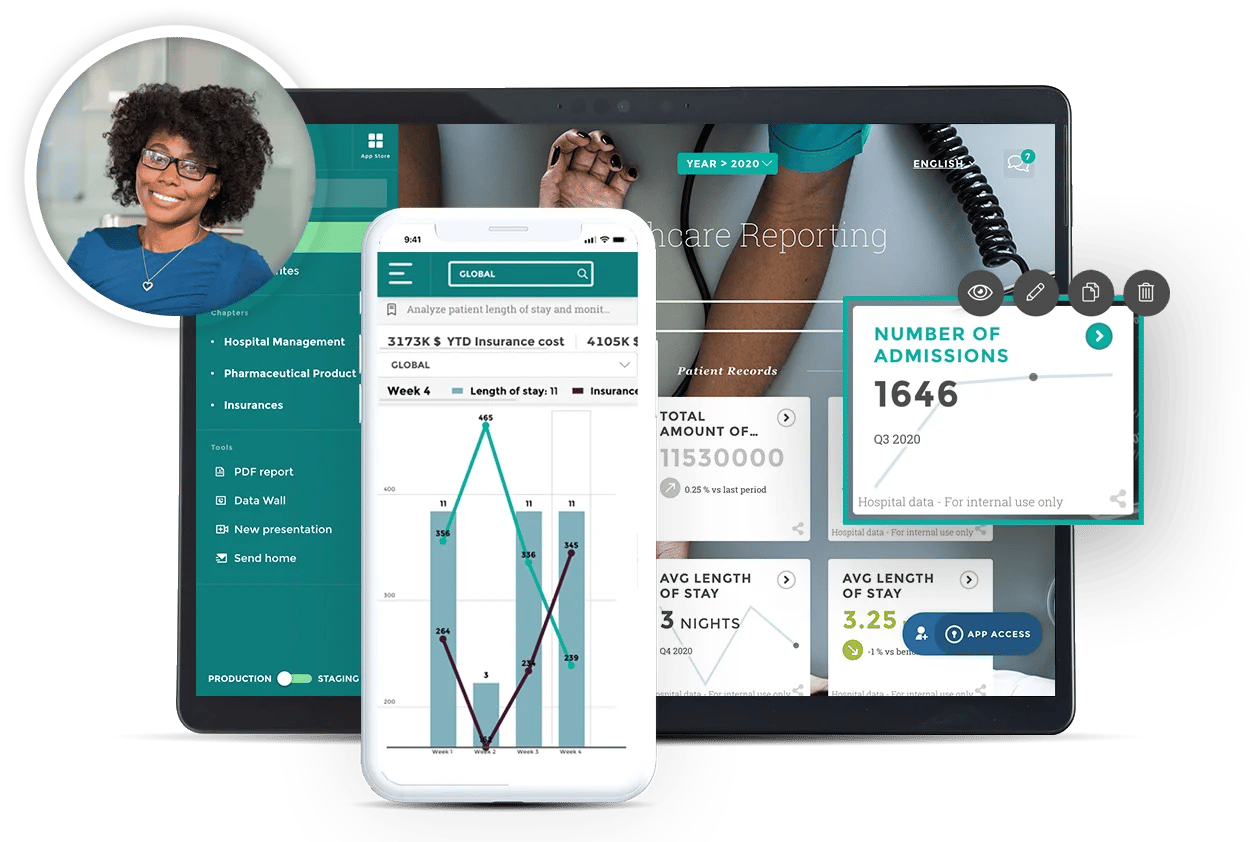
Core Capabilities:
- Provides a 360-degree view of the customer
- Data visualization
- Automated reporting
- Integrations with other data sources and platforms
- Data quality management
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Performance management
- Ad-hoc analysis
- Simulation models
- Budgeting
Product Analytics
Product analytics is a comprehensive set of tools that allow product managers and product teams to assess the performance of their digital experiences. Analysis of product performance provides critical information for optimizing performance, diagnosing problems, and identifying the long-term value of customer activity.
A product analytics software package provides you with the tools to gain a deeper understanding of what is occurring within the product. In addition to assessing customer experiences, you can optimize the performance of product usage, diagnose problems in your customer experience, correlate customer activity with lifetime value, and a great deal more.
Core Capabilities:
- Provides a 360-degree view of the product
- Connects with singular data sources
- Performance management
- Ad-hoc analysis
- Simulation models
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs)
Similarly to a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platform, a Customer Data Platform (CDP) collects and analyzes customer data for the purpose of improving processes and selling products. In contrast, CDPs take things to the next level when it comes to business continuity planning.
As opposed to CRMs, which collect data based on intentional interactions (unless manually entered) -such as communications history, website visits, and purchasing patterns - CDPs collect data from anonymous visitors to websites and manage and track data both online and offline. As a result, they handle a variety of data types from a variety of sources.
Core Capabilities:
- Provides all around view of the customer
- Connects multiple data sources (1st, 2nd, 3rd-party data)
- Unifies customer data across all connected systems
- Improves targeting for marketing campaigns
Business Intelligence (BI)
Business intelligence (BI) is software that ingests business data and presents it in user-friendly views such as reports, dashboards, charts and graphs. Business intelligence tools enable users to access a variety of types of data, such as historical and current data, third-party and internal data, as well as semi-structured and unstructured data, such as social media information. By analyzing this information, users can gain insight into the performance of their business.
Even though these platforms are quite diverse, the goal of business intelligence tools is to help organizations become data-driven through processes such as data mining, predictive modeling, and natural language processing. It is also becoming increasingly apparent that non-technical users are able to access insights that were previously only accessible to IT professionals.
Core Capabilities:
- Data mining
- Forecasting
- Automated reporting
- Data quality management
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Performance management
- Ad-hoc analysis
- Simulation models
- Budgeting
Embedded Analytics
Embedded analytics is the integration of analytical capabilities and data visualizations into another software application.
An analytics platform embedded within a software application allows users to analyze the data within that application in real time through the use of reports and dashboards. This analysis will allow the end user to identify and mitigate issues and identify opportunities for growth.
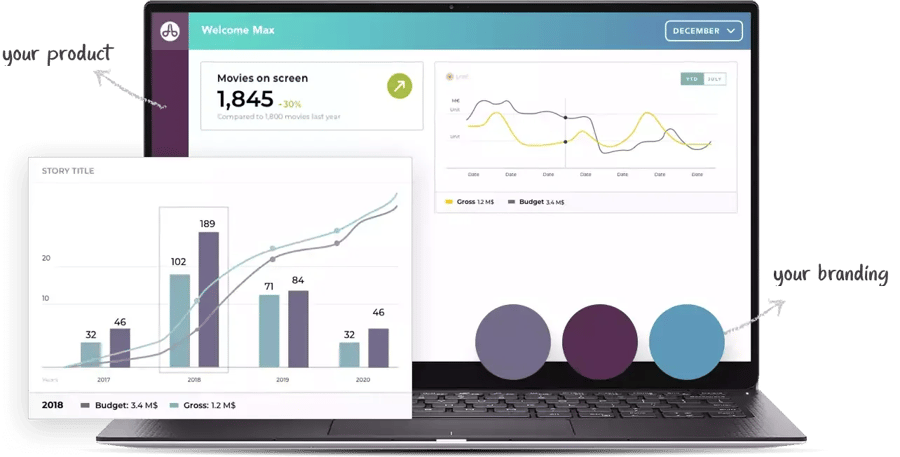
Analytics platforms that are embedded into software applications may not be recognized by end users as separate applications. Known as white labeling, this process involves rebranding the analytics platform to blend in with the look and feel of the application into which it is embedded. By doing so, enterprise applications can market the analytics as their own. In an alternative scenario, the analytics platform may be grey-labeled - retaining the brand name of the platform provider.
Core Capabilities:
- Data visualization
- Forecasting
- Automated reporting
- Integrations with other data sources and platforms
- Data quality management
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Performance management
- Ad-hoc analysis
Customer Analytics
A customer analytics tool is designed to assist in the management of the entire analytics process, from the preparation of data to the generation of insights. Analytic platforms for customer data usually include pre-built data models for forecasting, propensity to buy, and statistical analysis techniques to understand customer behavior and improve products, services, and experiences.
It is important to keep in mind that customer analytics platforms are more sophisticated than the tools that your marketing or sales department might use as they have extensive data visualizations. Although pre-built models make these platforms more accessible to non-technical users, you still need advanced data science skills in order to develop and run custom models or gain a complete understanding of the customer journey.
Core Capabilities:
- Granular segmentation
- Customer satisfaction insights
- Statistical modeling
- Acquisition, retention, and churn metrics
- Text analytics
- Extendable custom models built in R, Python or SAS
Digital Experience Platforms (DXPs)
An enterprise-grade Digital Experience Platform (DXP) optimizes customer experience at every touchpoint. Despite sharing some similarities with customer experience management (CXM) platforms, DXPs streamline processes and customize content across a variety of channels, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), digital assistants, and virtual reality. Marketing control over branding and content presentation is the main objective here.
Core Capabilities:
- API-first architecture
- Multi-touchpoint management
- Dynamic templates for automating personalization
- Content management and delivery
It should be noted that when it comes to data analytics platforms, we have really just scratched the surface. The main takeaway from this article is that in order to get the most out of your investments, you should have a clearly defined business case and strategy in place before investing in any solution.